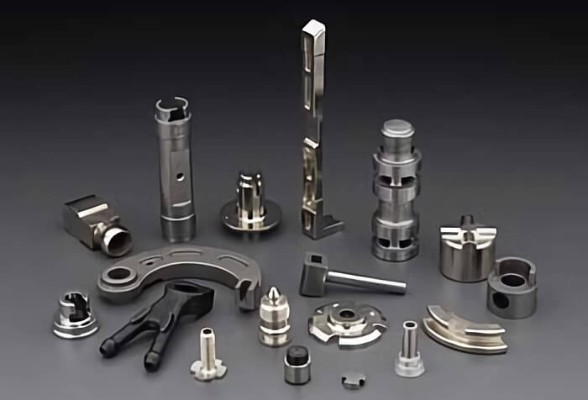
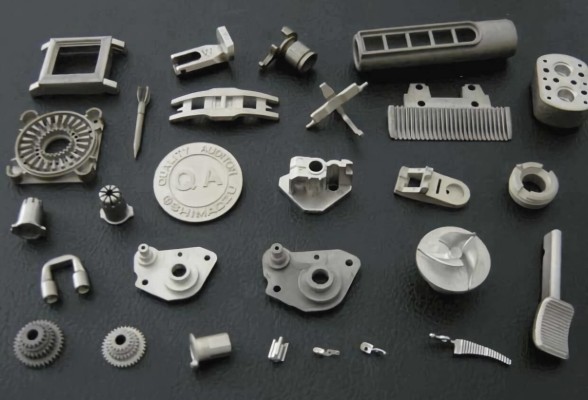
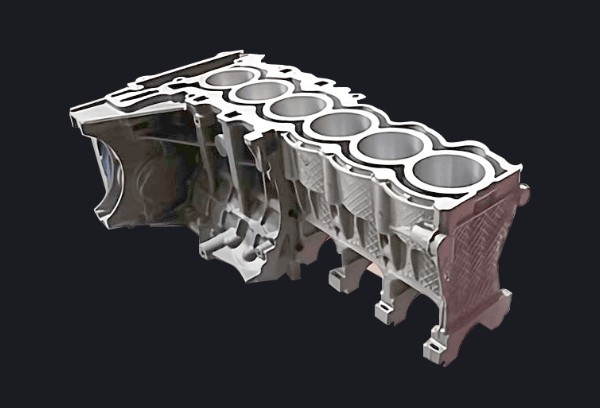
What Is Metal Injection Molding?
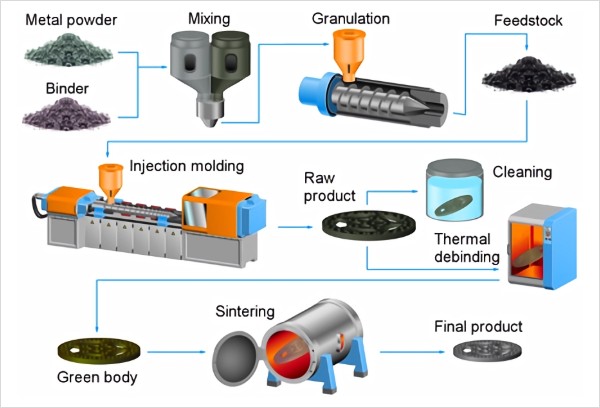
Metal injection molding (MIM) is a metal working process where metal powder bound is injected to a
thermoplastic binder to produce high-strength metal parts. The process adapts the technique of injection
molding, but the MIM parts require additional processing steps to remove the binder and sinter the powder. It
facilitates the production of small, complex-shaped metal parts with outstanding mechanical properties.