-
Material
The common materials used in injection molding include
polyethylene, polystyrene, nylon, polypropylene, acrylonitrile
butadiene styrene (ABS) and polycarbonate. Compression molding
more often makes use of materials like diallyl phthalate (DAP),
thermoset polyester, epoxy, sheet molding compound (SMC), vinyl
ester, phenolics and silicone. In addition, the two processes also
differ in the way the raw plastic material is manipulated into the
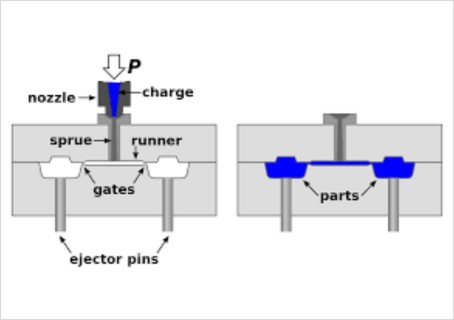
shape of the mold. Injection molding involves filling cavities
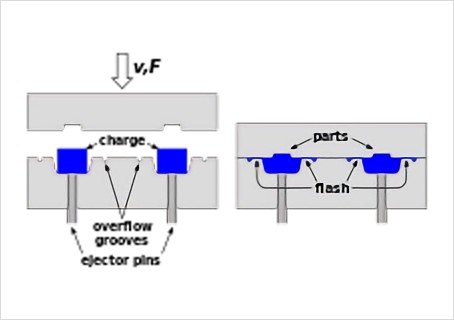
with melted plastic materials, while compression molding uses high
pressure and heat.
-
Speed
Injection molding is much faster than compression molding in that
its cycle time can be a few seconds. However, it takes a few
minutes for the compression molded parts in terms of cycle times
because of the need to cure .
-
Post-processing
As for injection molding, there is no need for post-processing.
However, post-processing is required for compression molding due
to the occurrence of flash.
-
The upfront costs
Due to the nature of the manufacturing process, the upfront costs
for injection molding are higher than that of compression molding.
-
Application
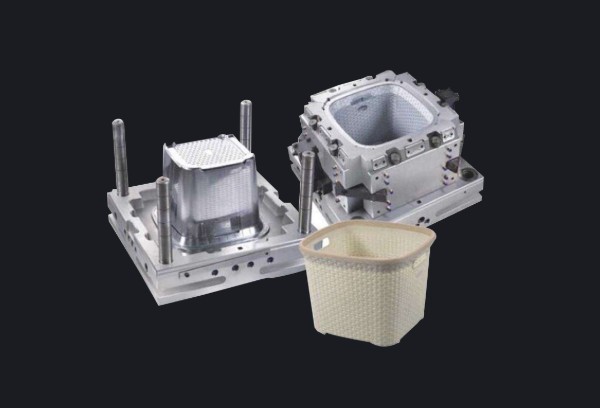
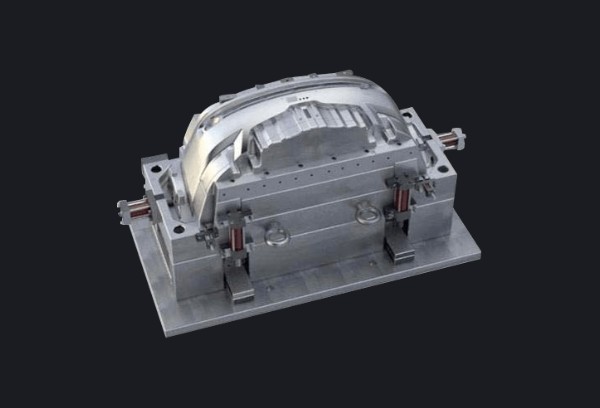
Injection molding is suitable for the high-volume production of
more intricate parts with a high degree of accuracy and
repeatability while compression molding is ideal for the
production of large, simple-shaped and durable ones.
-
Lead Time Length
The lead time for injection molding is significantly shorter as
opposed to compression molding .