What Is Squeeze Casting?
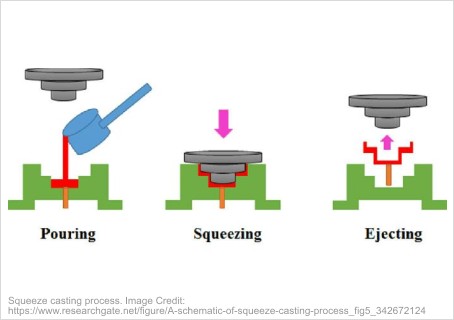
Squeeze casting, also known as liquid metal forging, is a
manufacturing process that combines casting and forging. It starts by
pouring the molten metal into a heated die. Then, the metal begins to
solidify, and the upper die is closed. With the pressure applied, the
casting cavities are completely filled with metal, which guarantees
accurate shape, minimal shrinkage and remarkable mechanical
properties. The process can be used to cast various metals. Aluminum
and magnesium alloys are most commonly used for the procedure.