What is Rotational Molding ?
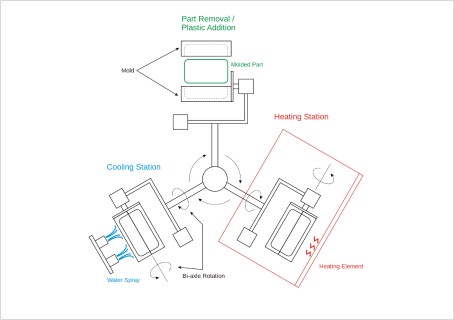
Rotational Molding Process Image Credit:
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rotational_molding
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rotational_molding
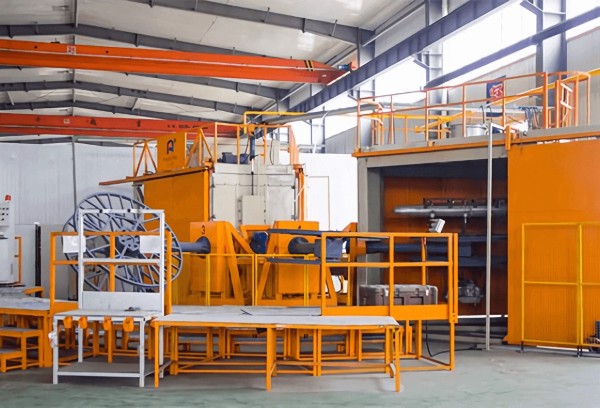
Rotational molding is a versatile manufacturing process used to
create hollow parts. It involves filling the heated mold with the
plastic powder. The mold is then rotated around two perpendicular
axes as it is heated.This makes the plastic melt, spread evenly
and coat the interior of the mold. The rotation continues during
both the heating and cooling phases, avoiding sagging or
deformation. After cooling, the material hardens, and the hollow
part with the desired shape can be removed from the
mold. Rotational molding can be more cost-effective when the
production demands are lower than 3,000 units a year. The process
can be used to form hollow parts with uniform wall
thickness,intricate geometries, and superior strength.